
In the Waves (Dans les Vagues)
Collection
Museum-quality reproductions on 310gsm textured cotton rag paper.
Shop all prints by Paul GauguinArtistic Style
Style Evolution
Gauguin moved from responses to Impressionism in Brittany—where he pared down detail and emphasized decorative shape—to a South Pacific period that embraced flattened space, symbolic subject matter, and a bold, non-naturalistic palette influenced by folk and non-Western traditions.
Palette
Subjects
Techniques
Topics
Paul Gauguin (1848-1903) was a French Post-Impressionist painter whose bold colors, flattened forms and turn to primitivism reshaped modern art.
Learn about the life of Paul Gauguin
Biography
Paul Gauguin (1848-1903) was a French Post-Impressionist painter whose bold colors, flattened forms and turn to primitivism reshaped modern art and inspired generations of avant-garde artists.
Paul Gauguin was born in Paris in 1848. After an early career in commerce and time at sea, he turned decisively to art in adulthood. His outsider status—partly shaped by travel, periods living in Brittany, and later life in the South Pacific—fed a restless search for new visual languages beyond academic naturalism.
Gauguin's career unfolded through distinct phases defined by place, experimentation, and a pursuit of simplified, symbolic form.
In Brittany he absorbed folk motifs and worked alongside younger painters seeking alternatives to Impressionism. He developed stronger contours, decorative patterning, and a palette that moved away from strict optical realism.
Gauguin's travels to Tahiti and later to the Marquesas Islands marked a decisive shift: he embraced so-called “primitive” subjects, symbolic narratives, and a more emblematic, flattened pictorial space that rejected European illusionism.
Gauguin is celebrated for pioneering a decorative, symbolic approach to painting that emphasized strong outlines, areas of pure color, and evocative, often mythic subject matter. His restless experimentation helped establish Post-Impressionism as a broad field that expanded modern art's expressive possibilities.
Gauguin favored simplified, flat planes of color, expressive contour lines, and a decorative surface rhythm. He often combined influences from European avant-garde movements and non-Western visual sources, using deliberate color contrasts and stylized forms to convey mood and narrative rather than naturalistic detail.
Gauguin’s work helped catalyze Primitivism and Symbolism in modern art and strongly influenced artists such as Henri Matisse and Pablo Picasso. His emphasis on color as expressive language and on formal simplification informed successive generations of modernists and decorative arts.
Gauguin’s life was marked by periods of financial instability, extensive travel, and an ongoing search for cultural alternatives to metropolitan European life. These personal circumstances were inextricable from his artistic experimentation.
Collectors prize Gauguin for his pioneering role in modernism, the decorative and emotive power of his canvases, and their cultural impact. His paintings remain highly sought after for museum collections and private buyers who value works that make a strong visual statement and anchor interiors with color, pattern, and exoticized narrative.
Frequently Asked Questions

In the Waves (Dans les Vagues)

Still Life with Profile of Laval
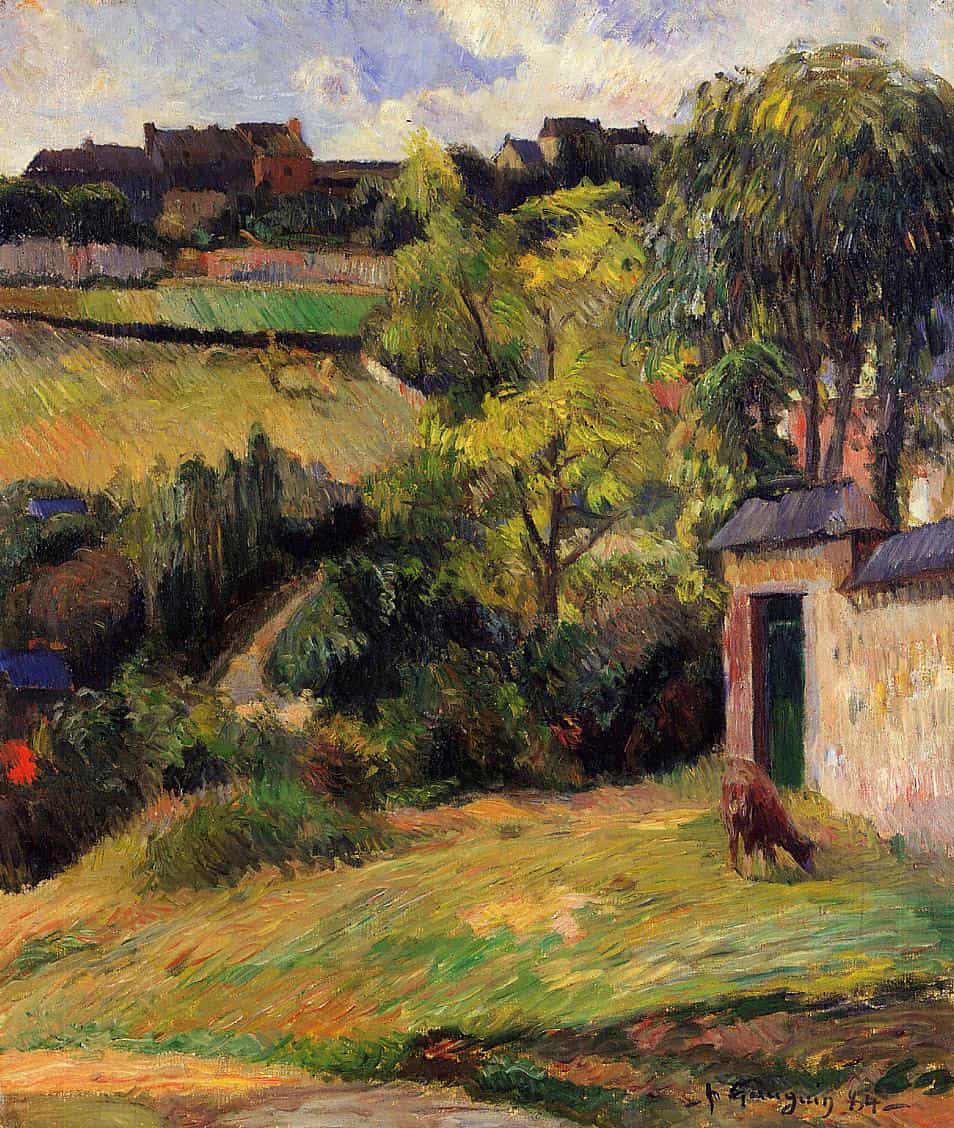

Rouen Suburb

The Large Tree

Breton Haymakers

unknown

Fa'aara
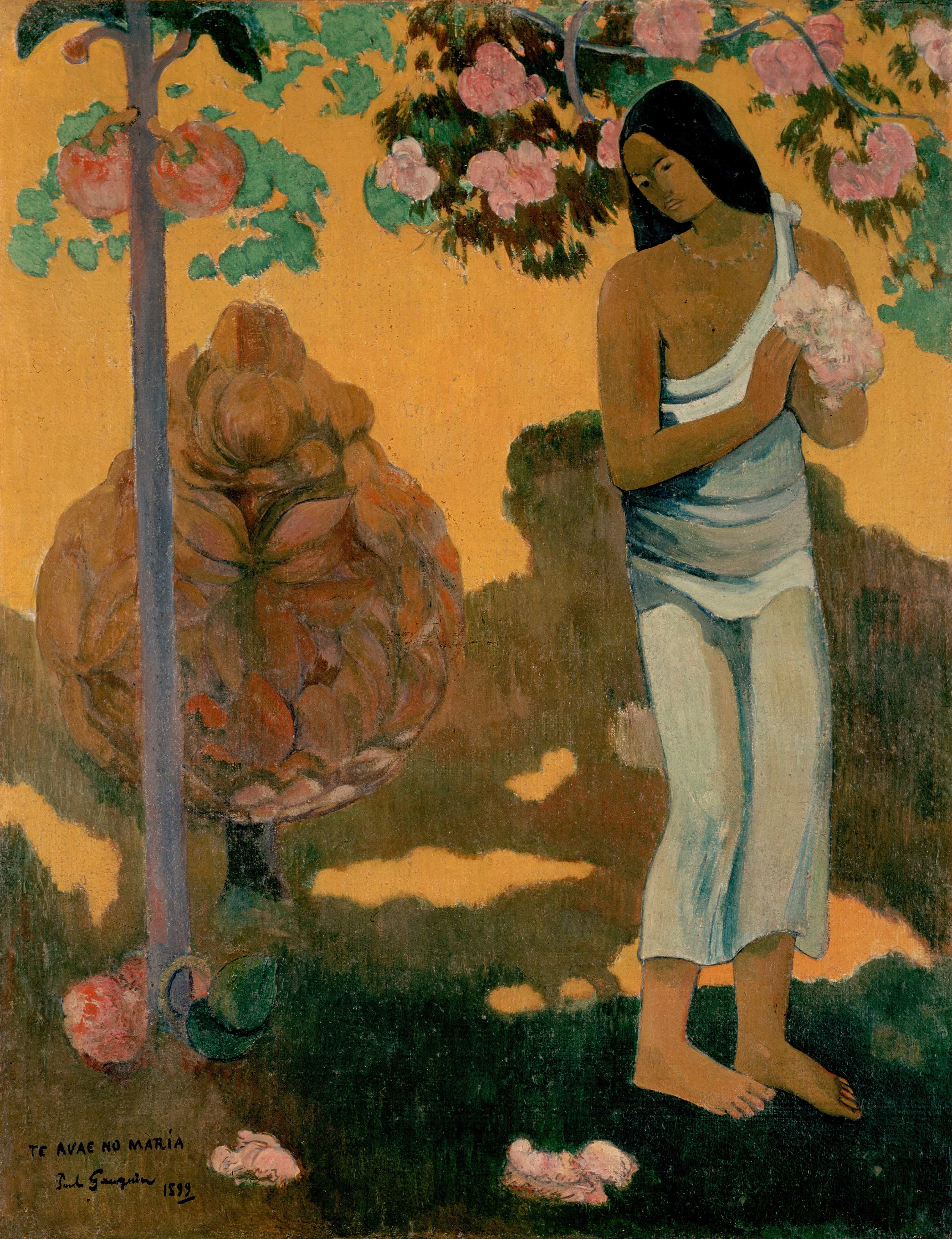

Month of Mary (Te avae no Maria)
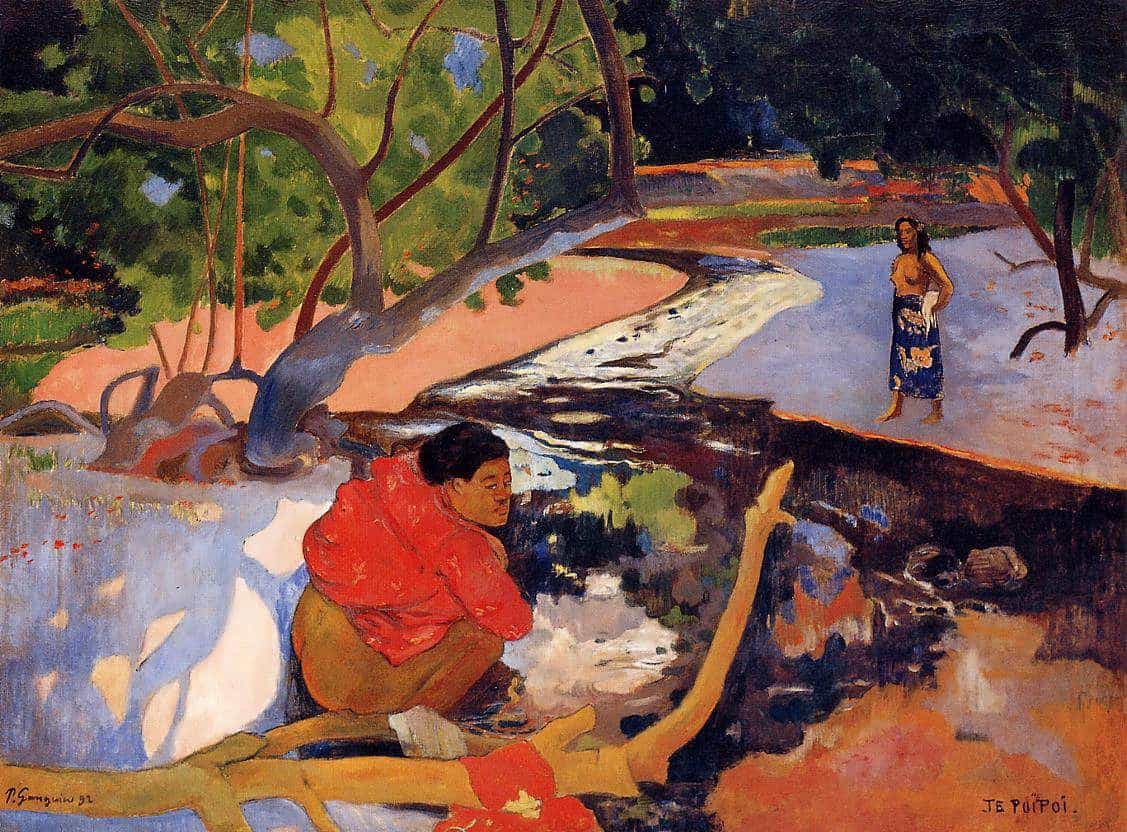

Te Poipoi

Hut of Songs
Coast at Dieppe

The Guitar Player